Modelled Stucture
Method:Homology modeling
Teplate PDB:6JPA_C
Identity:72.951%
Minimized Score:-919.207
Detail: Structure Info
| General Information of Drug Transporter (DT) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DT ID | DTD0535 Transporter Info | ||||
| Gene Name | CACNB2 | ||||
| Protein Name | Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel beta-2 | ||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| UniProt ID | |||||
| 3D Structure |
Modelled Stucture Method:Homology modeling Teplate PDB:6JPA_C Identity:72.951% Minimized Score:-919.207 Detail: Structure Info |
||||
| Inter-species Structural Differences (ISD) | |||||
| Bos taurus (Bovine) | |||||
| Gene Name | CACNB2 | ||||
| UniProt ID | |||||
| UniProt Entry | |||||
| 3D Structure |
Method:Homology modeling Teplate PDB:6JPA_C Sequence Length:412 Identity:76.611% |
||||
| Click to Save PDB File in TXT Format | |||||
| Performance | Minimized Score | -909.436 kcal/mol | |||
| Ramachandra Favored | Medium |
||||
| QMEANBrane Quality | Medium |
||||
| Ramachandran Plot |
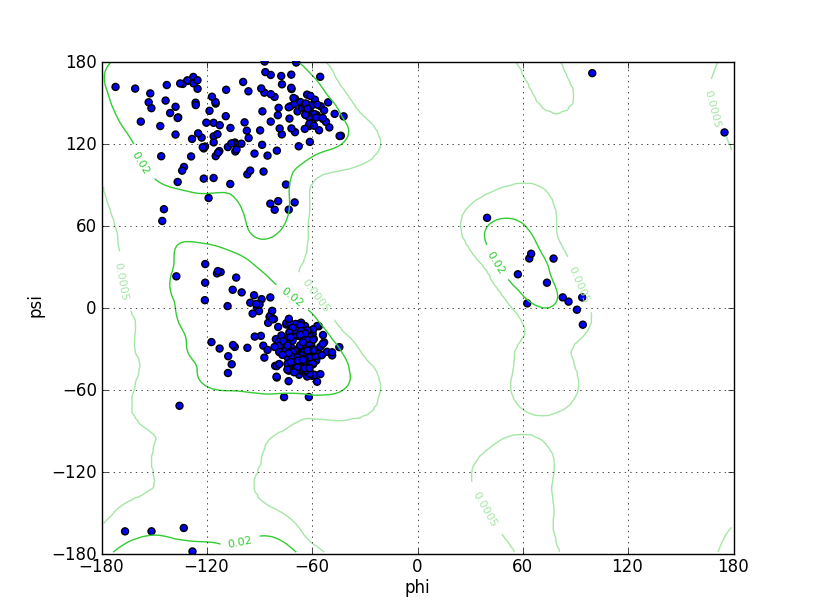
Ramz Z Score:-0.28 ±0.41 Residues in Favored Region:398 Ramachandran favored:97.07% Number of Outliers:2 Ramachandran outliers:0.49% |
||||
| Click to Save Ramachandran Plot in PNG Format | |||||
| Local Quality |
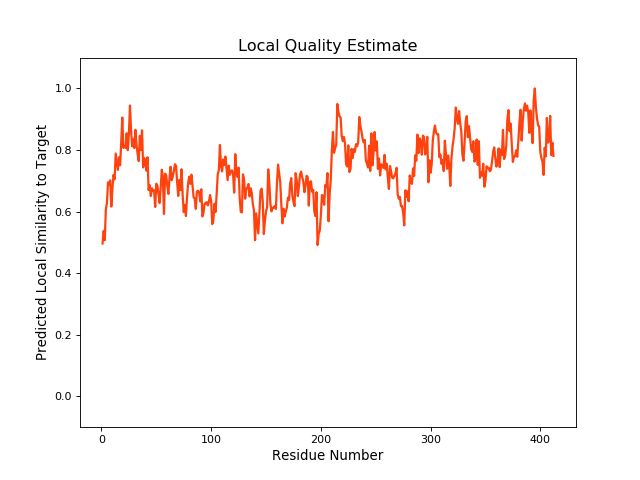
QMEANBrane Score:0.73 |
||||
| Click to Save Local Quality Plot in PNG Format | |||||
| References | |||||
| 1 | Structure of a complex between a voltage-gated calcium channel beta-subunit and an alpha-subunit domain. Nature. 2004 Jun 10;429(6992):671-5. | ||||
| 2 | Stapled Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel (Ca(V)) -Interaction Domain (AID) Peptides Act As Selective Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors of Ca(V) Function. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017 Jun 21;8(6):1313-1326. | ||||
| 3 | Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 complex. Science. 2015 Dec 18;350(6267):aad2395. | ||||
| 4 | The role of a voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel intracellular linker: a structure-function analysis. J Neurosci. 2012 May 30;32(22):7602-13. | ||||
| 5 | Structural analysis of the voltage-dependent calcium channel beta subunit functional core and its complex with the alpha 1 interaction domain. Neuron. 2004 May 13;42(3):387-99. | ||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Li and Dr. Fu.