Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00174
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Tenofovir
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(R)-9-(2-Phosphonomethoxypropyl)adenine; (R)-9-(2-Phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine; (R)-PMPA; Apropovir; D,L-Tenofovir; GNA & Tenofovir; GS 1275; GS 1278; GS1278; HHA & Tenofovir; KS-5021; PMPA; PMPA-(R); Phosphonic acid, [[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]-& Galanthus nivalis agglutinin (GNA); Phosphonic acid, [[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]-& Hippeastrum hybrid agglutinin(HHA); Phosphonic acid, [[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]-(9CI); Phosphonic acid, [[2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9; TDF; TFV; Tenefovir; Viread (TN); Viread, Tenofovir; [(2R)-1-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)propan-2-yl]oxymethylphosphonic acid
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD11:1C62.Z] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anti-HIV Agents
|
|||||
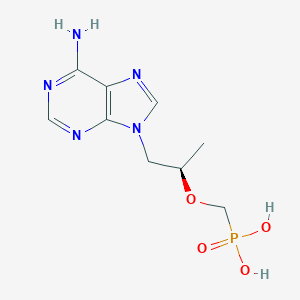
| Structure |
|
 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C9H14N5O4P
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(CN1C=NC2=C(N=CN=C21)N)OCP(=O)(O)O
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C9H14N5O4P/c1-6(18-5-19(15,16)17)2-14-4-13-7-8(10)11-3-12-9(7)14/h3-4,6H,2,5H2,1H3,(H2,10,11,12)(H2,15,16,17)/t6-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
SGOIRFVFHAKUTI-ZCFIWIBFSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 147127-20-6
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 287.21 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 136 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 | Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |||
| XLogP |
-1.6
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
102979961
,10304546
,103169192
,109738216
,12014981
,121362228
,124757224
,125164028
,126610616
,126628295
,126655803
,127310209
,127310210
,127339001
,127339002
,129233080
,134337989
,135078595
,135606020
,135611180
,135682533
,135698226
,136367764
,136372374
,136905481
,137005935
,141613622
,14873257
,151996120
,152034360
,152165365
,152246774
,152344570
,160963648
,162184452
,162793588
,163658367
,163813066
,171563543
,3727050
,3727057
,46508131
,48424314
,50112788
,50437671
,57405565
,610434
,7980754
,92719253
,99437132
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:63625
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | BCRP | Transporter Info | Breast cancer resistance protein | Substrate | [2] | |
| MRP4 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| MRP7 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 7 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| MRP8 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 8 | Substrate | [5] | ||
| OAT1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporter 1 | Substrate | [6] | ||
| OAT3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporter 3 | Substrate | [7] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [8] | ||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | ||||||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | OAT1 | Transporter Info | Km =33.8 microM | Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells-OAT1 | [6] | |
| OAT3 | Transporter Info | Km =770 microM | BHK-21 cells-OAT3 | [9] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Tenofovir was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D353-D361. (dg:DG01913) | |||||
| 3 | Functional involvement of multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) in the renal elimination of the antiviral drugs adefovir and tenofovir. Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Feb;71(2):619-27. | |||||
| 4 | Genetic variants of ABCC10, a novel tenofovir transporter, are associated with kidney tubular dysfunction. J Infect Dis. 2011 Jul 1;204(1):145-53. | |||||
| 5 | Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Is a New Substrate of ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Mar 24;61(4). pii: e01725-16. | |||||
| 6 | Human renal organic anion transporter 1 (hOAT1) and its role in the nephrotoxicity of antiviral nucleotide analogs. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2001 Apr-Jul;20(4-7):641-8. | |||||
| 7 | Tenofovir alafenamide is not a substrate for renal organic anion transporters (OATs) and does not exhibit OAT-dependent cytotoxicity. Antivir Ther. 2014;19(7):687-92. | |||||
| 8 | KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D353-D361. (dg:DG01665) | |||||
| 9 | Novel nucleotide human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase inhibitor GS-9148 with a low nephrotoxic potential: characterization of renal transport and accumulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Jan;53(1):150-6. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Li and Dr. Fu.
