Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR01165
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Gatifloxacin
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(+-)-1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; AM 1155; AM-1155; AM-1155 (*Sesquihydrate*); BMS 206584-01; BMS-206584; BMS-206584-01; Bonoq; CG 5501;PD 135432; CG-5501; GTFX; Gaity; Gatiflo; Gatiflo (TN); Gatiflo,Tequin and Zymar, Gatifloxacin; Gatifloxacin & Gamma Interferon; Gatifloxacin (INN); Gatifloxacin (TN); Gatifloxacin [USAN:INN]; Gatilox; Gatiquin; Gatispan; PD-135432; PD135432; Tequin; Tequin (TN); Tequin in dextrose 5% in plastic container; Zymar; Zymar (TN); Zymaxid; Zymer; Zymer (TN)
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Bacterial infections [ICD11:1A00-1H0Z] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinfective Agents
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
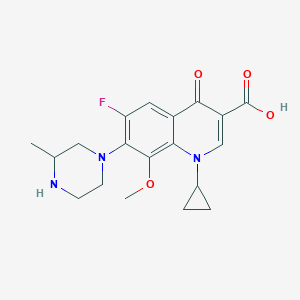 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C19H22FN3O4
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1CN(CCN1)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2OC)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C4CC4)F
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H22FN3O4/c1-10-8-22(6-5-21-10)16-14(20)7-12-15(18(16)27-2)23(11-3-4-11)9-13(17(12)24)19(25)26/h7,9-11,21H,3-6,8H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
XUBOMFCQGDBHNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 112811-59-3
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 375.4 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.1 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |||
| XLogP |
-0.7
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
103165247
,103905240
,104011321
,104170200
,11364853
,11367415
,11369977
,11372016
,11374751
,11378145
,11484089
,11488303
,11490814
,11492941
,11495723
,12014137
,14755600
,25623206
,26612698
,26680481
,26719627
,26748958
,26748959
,29224431
,3206265
,4404784
,46386695
,46506159
,47662548
,47736764
,49831421
,50068220
,50123177
,57322743
,618409
,642042
,77936610
,7979373
,8153306
,85279062
,85789262
,861394
,87322631
,92124759
,92307956
,92309206
,92711370
,96024704
,9863
,99437219
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:5280
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | MRP2 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 | Substrate | [2] | |
| OATP1A2 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1A2 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Gatifloxacin was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Uptake and intracellular release kinetics of liposome formulations in glioma cells. Int J Pharm. 2010 Aug 16;395(1-2):251-9. | |||||
| 3 | Identification of influx transporter for the quinolone antibacterial agent levofloxacin. Mol Pharm. 2007 Jan-Feb;4(1):85-94. | |||||
| 4 | Interaction of gatifloxacin with efflux transporters: a possible mechanism for drug resistance. Int J Pharm. 2010 Aug 16;395(1-2):114-21. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Li and Dr. Fu.
