Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00523
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Crizotinib
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Xalkori (TN); novel ALK inhibitors
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD11:2C25] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
|
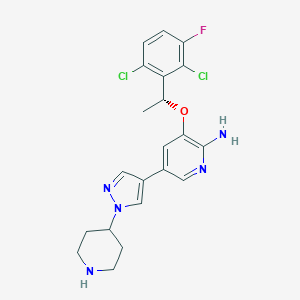 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C21H22Cl2FN5O
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C1=C(C=CC(=C1Cl)F)Cl)OC2=C(N=CC(=C2)C3=CN(N=C3)C4CCNCC4)N
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H22Cl2FN5O/c1-12(19-16(22)2-3-17(24)20(19)23)30-18-8-13(9-27-21(18)25)14-10-28-29(11-14)15-4-6-26-7-5-15/h2-3,8-12,15,26H,4-7H2,1H3,(H2,25,27)/t12-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
KTEIFNKAUNYNJU-GFCCVEGCSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 877399-52-5
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 450.3 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 78 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 | Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 | |||
| XLogP |
3.7
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
103728028
,104161043
,119526687
,121278669
,124490471
,124756975
,125163780
,125299329
,126659900
,131407280
,135264650
,135668295
,135727397
,136345871
,136367829
,136920405
,137232008
,137275901
,141226597
,143499147
,152040652
,152134626
,152237527
,152258843
,152344161
,160644611
,160647693
,160815247
,160969694
,162010188
,162010189
,162011538
,162196520
,162927269
,163565316
,163590241
,164041842
,164193931
,165245564
,16729581
,170497919
,174531154
,175265614
,23733583
,74374126
,75543391
,93581001
,99309272
,99437209
,99445171
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:64310
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 | Substrate | [2] | |
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Crizotinib was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Mar 15;19(6):1458-66. | |||||
| 3 | Increased oral availability and brain accumulation of the ALK inhibitor crizotinib by coadministration of the P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) inhibitor elacridar. Int J Cancer. 2014 Mar 15;134(6):1484-94. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Li and Dr. Fu.
