Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00242
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Glycine
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(1-13c)glycinato; (15N)Glycine; 2,2-dialkylglycines; 2-Aminoacetic acid; AB-131/40217813; AMINOACETIC ACID 1.5% IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; Acide aminoacetique; Acide aminoacetique [INN-French]; Acido aminoacetico; Acido aminoacetico [INN-Spanish]; Acidum aminoaceticum; Acidum aminoaceticum [INN-Latin]; Aciport; Aminoacetic acid; Aminoazijnzuur; Aminoessigsaeure; Aminoethanoic acid; Amitone; An alpha amino acid ester; Corilin; GLY (IUPAC abbrev); GLYCINE 1.5% IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; GLYCINE, ACS; Glicina; Glicina [INN-Spanish]; Glicoamin; Gly; Glycin; Glycine (JP15/USP); Glycine [INN]; Glycine iron sulphate (1:1); Glycine, homopolymer (VAN); Glycine, labeled with carbon-14; Glycine, non-medical; Glycine-UL-14C hydrochloride; Glycinum; Glycinum [INN-Latin]; Glycocoll; Glycolixir; Glycosthene; Glykokoll; Glyzin; Gyn-hydralin; H-Gly-OH; H2N-CH2-COOH; Hampshire glycine; Hgly; L-Glycine; L-alpha-amino acids; Leimzucker; Padil; Polyglycine; Polyglycine II; S04-0135; Sucre de gelatine
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Dietary shortage [ICD11:5B7Z] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Dietary supplement
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
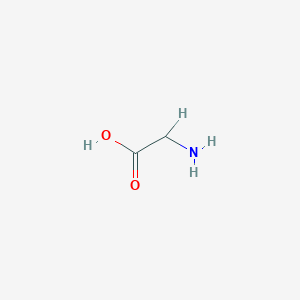 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C2H5NO2
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C(C(=O)O)N
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C2H5NO2/c3-1-2(4)5/h1,3H2,(H,4,5)
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 56-40-6
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 75.07 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 | Rotatable Bond Count | 1 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 | |||
| XLogP |
-3.2
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
10527483
,11113413
,11528254
,14747327
,16955354
,17404564
,24439112
,24775647
,24849510
,24860042
,24865701
,24873323
,24895210
,24895217
,24895290
,24895306
,24895353
,24895355
,24898980
,24901611
,26718882
,26751653
,3133349
,3339
,33728423
,37415007
,46295148
,585843
,589752
,626974
,6435754
,7346033
,7847079
,7887927
,7979426
,8026292
,8026825
,8138085
,8145759
,8150769
,827140
,829229
,829387
,830123
,833865
,836630
,836631
,838484
,841093
,86929
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:15428
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | ASCT2 | Transporter Info | Alanine/serine/cysteine/threonine transporter 2 | Substrate | [2] | |
| BGT1 | Transporter Info | Na(+)/Cl(-) betaine/GABA transporter | Substrate | [3] | ||
| GLYT1 | Transporter Info | Sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine transporter 1 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| GLYT2 | Transporter Info | Sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine transporter 2 | Substrate | [5] | ||
| LAT2 | Transporter Info | L-type amino acid transporter 2 | Substrate | [6] | ||
| PAT1 | Transporter Info | Proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 | Substrate | [7] | ||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | ||||||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | ASCT2 | Transporter Info | Km =320 microM | HRPE cells-ASCT2 | [2] | |
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Cannabidiol was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Transport of butyryl-L-carnitine, a potential prodrug, via the carnitine transporter OCTN2 and the amino acid transporter ATB(0,+). Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):G1046-53. | |||||
| 3 | Interpreting metabolomic profiles using unbiased pathway models. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Feb 26;6(2):e1000692. | |||||
| 4 | Mutation in SLC6A9 encoding a glycine transporter causes a novel form of non-ketotic hyperglycinemia in humans. Hum Genet. 2016 Nov;135(11):1263-1268. | |||||
| 5 | Mutations in the GlyT2 gene (SLC6A5) are a second major cause of startle disease. J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28975-85. | |||||
| 6 | The Transporter Classification Database (TCDB): recent advances. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D372-9. (ID: 2.A.3.8.20) | |||||
| 7 | Transport of amino acids and GABA analogues via the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter, hPAT1: characterization of conditions for affinity and transport experiments in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008 Sep 2;35(1-2):86-95. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Li and Dr. Fu.
